When initialize a new 3PAR, depending on your protection level, at least the size of one disk per disk-type will be reserved as spare. Also when you add disks to a running system, spare-chunklets are created. This is done by admithw. For example when you initialize a system containing 2 SSDs for adaptive flash cache (AFC) the size of one SSD is reserved for spare. […]
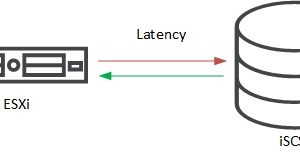
3PAR (iSCSI) – resolve high write latency on ESXi hosts
FC AFA (all flash array) 3PAR systems show quite a good latency on reads and writes. When operating an iSCSI AFA 3PAR it could happen that the systems show a rather high write latency on ESXi hosts. In this post you can read how to fix this.
simple linux Script to shut down VMs and ESXi host
Here is a very simple linux bash script to shut down all VMs of a ESXi host and the host itself, for example when a power failure occurs, this script can be used in UPS software. Some time ago a posted how to use such script in an HPE UPS environment. You can find the post here.
Backup from snapshot on target 3PAR
In a 3PAR Peer Persistence configuration volumes are synchronously replicated between two 3PAR arrays. For each volume one array acts as primary or source array. This array exports the volume for read/write. The other array acts as secondary or target for replication. For performance reasons it could be an advantage when backup reads data from target array. This is easily possible with Veeam B&R 9.5.
3PAR – does CPG setsize to disk-count ratio matter?
In a 3PAR system it is best practice that setsize defined in CPG is a divisor of the number of disks in the CPG. The setsize defines basically the size of a sub-RAID within the CPG. For example a setsize of 8 in a RAID 5 means a sub-RAID uses 7 data and one parity disk.
Remove a cage from a 3PAR array
To remove a cage from a 3PAR array can be a simple task. But it can also be impossible without help from HPE. Before starting at point 1, you should probably check point 3 first. Generally I would recommend to do any of these steps ONLY when your are very familiar to 3PAR systems! know what you are doing! know what are the consequences of […]
3PAR: Considerations when mixing sizes of same disk type
Generally it is supported to mix disks of different sizes of the same type within a 3PAR system. For example you can use 900GB and 1.2TB FC-disks – within the same cage and even within the same CPG. When a disk fails, HPE sends an replacement disk. Some time ago, stock of 900GB FC disks seem to be empty. So when a 900GB disk fails, […]
Error send to root account in ESXi
On a HPE Proliant Server upgraded to ESXi 6.0 U3 image: VMware-ESXi-6.0.0-Update3-6921384-HPE-600.10.2.0.23-Feb2018.iso I get the error sent to root-account: WorldList: malloc failed when allocating allNodes list So, you can see the error every few minutes when you logged in to console or using SSH. In /var/log/vmkernel.log you can see this error: User: 3820: sfcb-intelcim: wantCoreDump:sfcb-intelcim signal:6 exitCode:0 coredump:disabled This is caused by a problem with HPE […]
Create CPG using Disk Filter
Recently I had to create a new 3PAR CPG using just new added 1.2TB disks. But the system uses already a cage full of 600GB disk. While it was straight forward to change the existing CPG (using 3PAR Management Console) – StoreServe Management Console (SSMC) does not support this feature any more) to use all disk in cage 0, it was not possible to create a […]
How PDL (Permanent Device Loss) looks like
Some time ago differentiation between PDL (Permanent Device Loss) and APD (All Path Down) was introduced to vSphere. In a PDL situation, the hosts does not expect the device to return. PDL happens for example, when an administrator un-presents a LUN from a host. APD on the other hand is completely unplanned. By default the host tries to get the device back. Starting with vSphere […]