3-2-1 rule for Veeam configuration backup
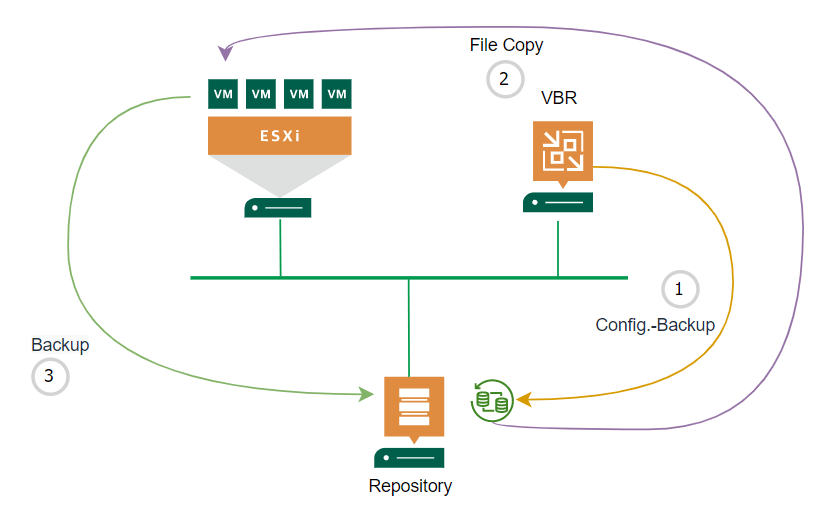
There is the widely known rule for backups: the 3-2-1 rule. Basically it says: keep 3 copies of your data on 2 different media with 1 copy being off site. Backup administrators should apply this rule to their backup configuration of production workload. As best practice, apply the 3-2-1 rule for Veeam configuration backup too.
Veeam configuration backup
By default, Veeam Backup&Replication (VBR) does a configuration backup every day at 10:00. If not configured otherwise, default Repository is selected as target.
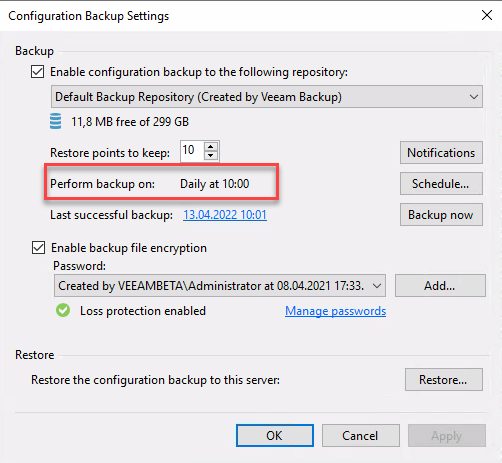
Because you can define the numbers of restore points to keep, volume should not get full because of these files. To comply with the 3 of 3-2-1 rule, the target folder must be copied to another location. This can be done by a custom script or by a Veeam File Copy job. Because the second option is very simple, I will it show here.
Using File Copy job
An easy way to comply with 2 and 1 in the 3-2-1 rule is to copy these restore points to a machine that is already backed up be Veeam and therefore covered by the 3-2-1 rule. A Veeam File Copy job can copy files between systems part of Managed Servers.
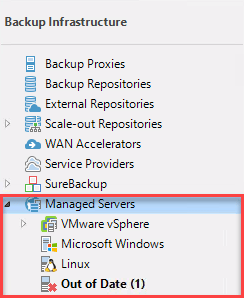
So it would be also possible to copy Veeam configuration backups to a Linux system, if this helps. Lets create a File Copy job. To do click Copy Job and File…
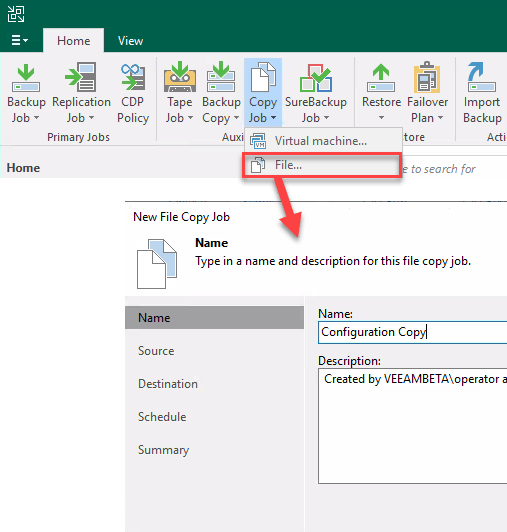
Wizard is self-explanatory. As source select the folder of configuration backup. For target choose a folder of a server that is already covered by the 3-2-1 rule. Finally select your preferred time schedule. I would recommend to run this job just after the configuration backup.
Done? Almost! It is important to know, File Copy job copies files respectively a directory, but is does not synchronize. Therefore the amount of files at the destination will increase. So they should get deleted after some time otherwise volume runs full. A easy way to do this is to schedule a PowerShell script like this:
$DeleteData = (Get-Date).AddDays(-14).Date
Get-ChildItem -Path E:\Copy_VeeamBackupConfig\VeeamConfigBackup\*\*.bco | Where-Object {$_.CreationTime -lt $DeleteData} | Remove-Item
Security
An advantage of using File Copy job here is that you do not have to care about user authentication for the target system. This is because VBR does this for you. And so it is possible to use a local non-administrative user account for removing old files – like in the script before – on the target system.
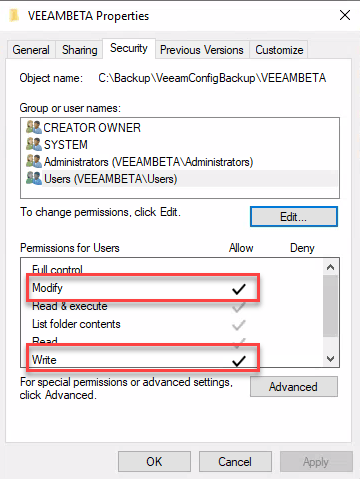
Keep in mind, in case of a Windows target, Veeam File Copy job also copies file permissions (ACL)! To enable a user-account at the destination system to delete old restore points, files at both sides (source and destination) must have write/modify permission for the group users.
Conclusion
The backup 3-2-1 rule should be applied on every backup and on Veeam configuration backup too. In this post I showed how this can be done by using the built-in File Copy job. This is not the only way. Therefore I want to finsh with some advantages and disadvantages of this solution.
Advantages
- Copy files without custom script. Therefore no authentication handling in script is necessary.
- Target can be any Windows/Linux system listed beneath Managed Systems.
- Copy Job can be monitored in same console as every other Veeam VBR backup.
- Retention of copied files can be done by a non-administrative user.
Disadvantages
- Because File Copy job does not support any kind of retention, old files must be deleted separately. This can be done with an simple local script.
Notes
- Get your trial of Veeam Backup&Replication!
- Did you know, you can copy a backup copy job too?


